74 lines
3.5 KiB
Markdown
74 lines
3.5 KiB
Markdown
|
|
---
|
||
|
|
title: Creating your own providers
|
||
|
|
---
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Creating your own Providers
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Providers in CloudStream consists primarily of 4 different parts:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
- [Searching](/dokka/app/com.lagradost.cloudstream3/-main-a-p-i/index.html#498495168%2FFunctions%2F492899073)
|
||
|
|
- [Loading the home page](/dokka/app/com.lagradost.cloudstream3/-main-a-p-i/index.html#1356482668%2FFunctions%2F492899073)
|
||
|
|
- [Loading the show page](/dokka/app/com.lagradost.cloudstream3/-main-a-p-i/index.html#1671784382%2FFunctions%2F492899073)
|
||
|
|
- [Loading the video links](/dokka/app/com.lagradost.cloudstream3/-main-a-p-i/index.html#-930139416%2FFunctions%2F492899073)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
When making a provider it is important that you are confident you can scrape the video links first!
|
||
|
|
Video links are often the most protected part of the website and if you cannot scrape them then the provider is useless.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
## 0. Scraping
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
If you are unfamiliar with the concept of scraping, you should probably start by reading [this guide](../scraping/index.md) which should hopefuly familiarize you with this technique.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
## 1. Searching
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
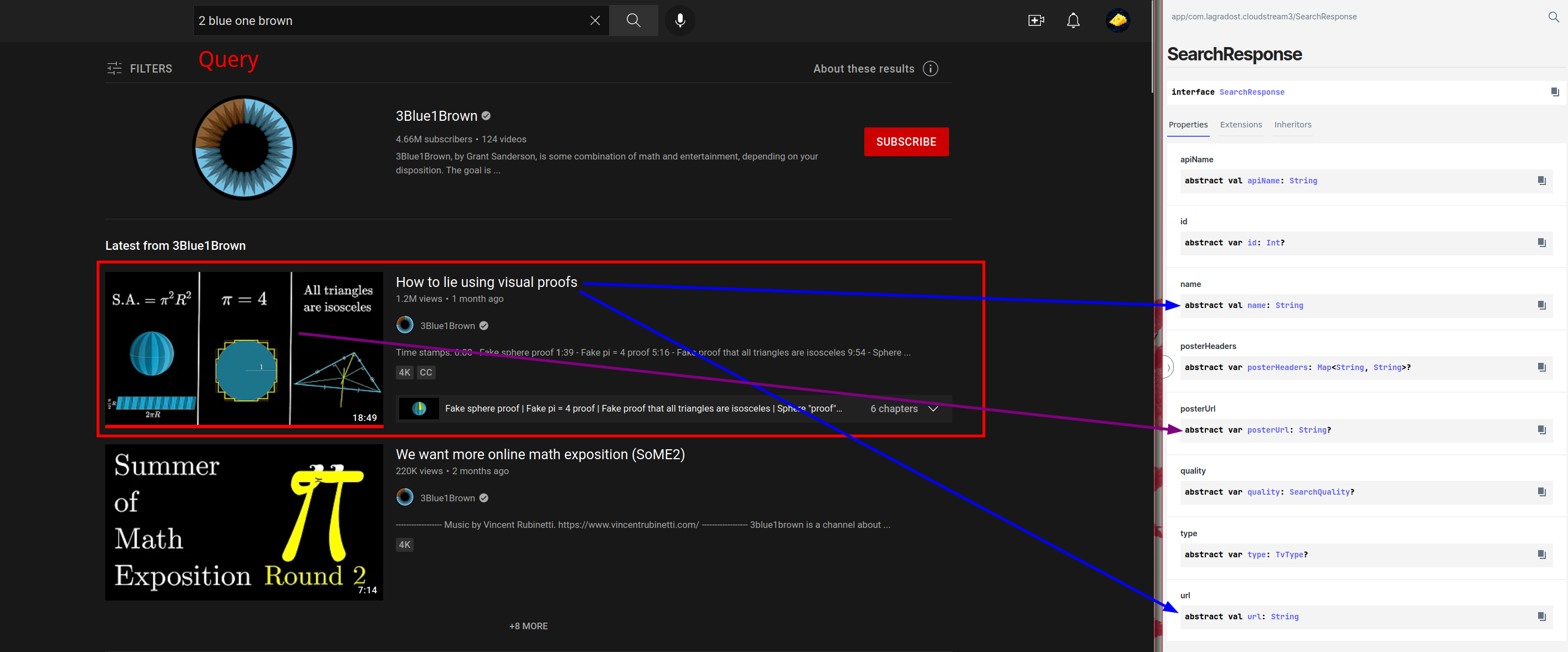
This one is probably the easiest, based on a query you should return a list of [SearchResponse](/dokka/app/com.lagradost.cloudstream3/-search-response/index.html)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Scraping the search results is essentially just finding the search item elements on the site (red box) and looking in them to find name, url and poster url and put the data in a SearchResponse.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
The code for the search then ideally looks something like
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```kotlin
|
||
|
|
// (code for Eja.tv)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
override suspend fun search(query: String): List<SearchResponse> {
|
||
|
|
return app.post(
|
||
|
|
mainUrl, data = mapOf("search" to query) // Fetch the search data
|
||
|
|
).document // Convert the response to a searchable document
|
||
|
|
.select("div.card-body") // Only select the search items using a CSS selector
|
||
|
|
.mapNotNull { // Convert all html elements to SearchResponses and filter out the null search results
|
||
|
|
it.toSearchResponse()
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// Converts a html element to a useable search response
|
||
|
|
// Basically just look in the element for sub-elements with the data you want
|
||
|
|
private fun Element.toSearchResponse(): LiveSearchResponse? {
|
||
|
|
// If no link element then it's no a valid search response
|
||
|
|
val link = this.select("div.alternative a").last() ?: return null
|
||
|
|
// fixUrl is a built in function to convert urls like /watch?v=..... to https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=.....
|
||
|
|
val href = fixUrl(link.attr("href"))
|
||
|
|
val img = this.selectFirst("div.thumb img")
|
||
|
|
// Optional parameter, scraping languages are not required but might be nice on some sites
|
||
|
|
val lang = this.selectFirst(".card-title > a")?.attr("href")?.removePrefix("?country=")
|
||
|
|
?.replace("int", "eu") //international -> European Union 🇪🇺
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
// There are many types of searchresponses but mostly you will be using AnimeSearchResponse, MovieSearchResponse
|
||
|
|
// and TvSeriesSearchResponse, all with different parameters (like episode count)
|
||
|
|
return LiveSearchResponse(
|
||
|
|
// Kinda hack way to get the title
|
||
|
|
img?.attr("alt")?.replaceFirst("Watch ", "") ?: return null,
|
||
|
|
href,
|
||
|
|
this@EjaTv.name,
|
||
|
|
TvType.Live,
|
||
|
|
fixUrl(img.attr("src")),
|
||
|
|
lang = lang
|
||
|
|
)
|
||
|
|
}
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
In this code snippet I have separated the Element to SearchResult conversion to a separate function because that function can often be used when scraping the home page later. No need to parse the same type of element twice.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# TODO REST
|